Electric flux: Problems with Solutions for AP Physics
Dive into our self-tutorial problems and solutions on electric flux, designed for both uniform and non-uniform fields. Ideal for AP Physics C exam prep and college students seeking to strengthen their understanding.
The AP Physics exams are just around the corner! Get our comprehensive 31-page equation sheet and ace the AP Physics 1 Exam in $2025$. Limited time offer for just $\$ 10$! (Download free PDF sample).
The electric flux of uniform electric fields:
Problem (1): A uniform electric field with a magnitude of $E=400\,{\rm N/C}$ incident on a plane with a surface of area $A=10\,{\rm m^2}$ and makes an angle of $\theta=30^\circ$ with it. Find the electric flux through this surface.
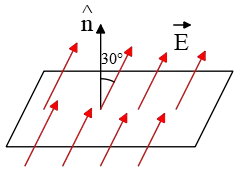
Solution: electric flux is defined as the amount of electric field passing through a surface of area $A$. The formula for electric flux is \[\Phi_e=\vec{E} \cdot \vec{A}=E\, A\,\cos\theta \] where dot ($\cdot$) represents the dot product between electric field and area vector, and $\theta$ is the angle between $\vec{E}$ and the normal vector $\hat{n}$ (a vector of magnitude one and perpendicular to the surface) to the plane.
In this problem, the angle between the electric field and the normal to the plane is $30^\circ$ Therefore, we get \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=EA\,\cos \theta\\&=400\times 10\times \underbrace{\cos 30^\circ}_{\sqrt{3}/2}\\&=\boxed{2000\sqrt{3}\quad {\rm N \cdot m^2/C}}\end{align*} Thus, the flux is nearly $\Phi=3464\,\rm N\cdot m^2/C$. Imagine the electric field lines as tiny arrows representing the electric field's strength and direction.
The flux tells you how many of these arrows pass through the surface every second. In this case, around $3464$ arrows pass through the $\rm 10\,m^2$ surface each second.
If this page helped you with homework or anything else, please support me here.
Problem (2): Find the electric flux through the surface with sides of $15\,{\rm cm}\times 15\,{\rm cm}$ positioned in a uniform electric field of $E=150\,\rm N/C$ as shown in the figure below.

Solution: First, determine the angle between the electric field and the normal vector, $\hat{n}$, which is perpendicular to the plane and directed upward.
In this problem, the electric field forms a $30^\circ$ angle with the plane. However, we cannot simply state that the angle between $\vec{E}$ and $\hat{n}$ is $90^\circ-30^\circ=60^\circ$. This is because the electric field vector points into the surface, while the normal vector is directed out of the plane.
In such cases, to find the angle with the unit vector perpendicular to the surface (or normal vector), we first coincide the tails of two vectors and then determine the required angle, which in this case is $\theta=90^\circ+30^\circ=120^\circ$. A side view of the angle between the electric field and the normal vector to the surface is shown in the figure below.
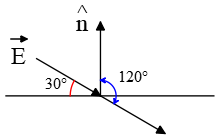
Next, using the definition of electric flux, $\Phi_e=EA\,\cos \theta$, we find that \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=EA\,\cos \theta \\&=150\times (0.15)^{2}\times \cos 120^\circ\\&=\boxed{-1.125\quad {\rm N\cdot m^2/C}}\end{align*} The negative sign of the electric flux indicates that the electric field lines are entering the surface.
This means that about $1.125$ electric field lines are entering each square meter of the surface every second.
Problem (3): A square surface with sides of $\rm 1 m \times 1 m$ located over the $xy$-plane, where a constant electric field with a magnitude of $200\,{\rm N\cdot m^2/C}$ presents. The direction of the electric field vector is depicted in the figure. What is the total electric flux through the open surface?
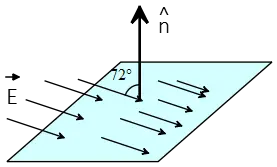
Solution: Since the electric field is constant and the surface is flat, we can use the electric flux formula $\Phi_e=EA\cos \theta$. Note that the given angle is not the angle we want to use in the flux formula. The correct angle between $\vec{E}$ and $\hat{n}$ is $180^\circ-72^\circ$ (refer to the previous problem). Therefore, the electric flux through the surface is \begin{align*} \Phi_E &=E\,A\,\cos \theta\\&=200\times (1)^2 \times \cos (180^\circ-72^\circ) \\&=\boxed{-61.8\quad {\rm N\cdot m^2/C}}\end{align*} The negative electric flux indicates that $\vec{E}$ and the normal vector are in the opposite directions. The following figure indicates how to calculate the angle between a vector perpendicular to the surface (normal vector) and the electric field vector.
The blue, two-headed arrow represents the correct angle between $\hat{n}$ and $\vec{E}$.
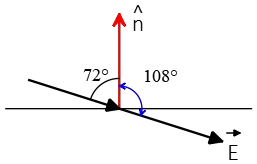
Note: Always remember that the angle between the electric field ($\vec{E}$) and its normal vector $\hat{n}$ is the angle formed by the tails of the two vectors. This means the vectors should be placed together tail-to-tail to measure the angle correctly. In the previous two problems, there might have been confusion due to not carefully considering the tail-to-tail placement of the vectors.
Problem (4): In the figure below, a flat surface of sides $\rm 10\, cm \times 50\, cm$ is positioned in the presence of a uniform electric field of unknown strength. The electric flux through this surface is $250\,\rm N\cdot m^2/C$. What is the strength of the electric field?
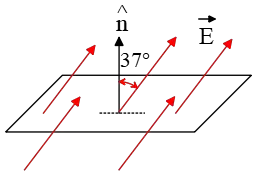
Solution: The area of the rectangular surface is calculated as \[A=0.1\times 0.5=0.05\quad \rm m^2\] Since $\vec{E}$ and $\hat{n}$ are positioned tail-to-tail in this scenario, we can be confident that the provided angle of $37^\circ$ accurately reflects the true angle between the electric field vector $\vec{E}$ and the surface's normal vector $\hat{n}$.
The magnitude of the flux is given as $\Phi_E=250\,\rm N\cdot m^2/C$. Substitute these numerical values into the electric flux formula and solve for the unknown field strength $E$: \begin{gather*} \Phi_E=EA\cos\theta \\\\ 250=E(0.05) \underbrace{\cos 37^\circ}_{0.8} \\\\ \Rightarrow \, E=\frac{250}{0.05\times 0.8} \\\\ \Rightarrow \boxed{E=6250\quad \rm N/C} \end{gather*} Thus, the electric field strength is $6.25\times 10^3 \,\rm N/C$ in scientific notation.
Problem (5): What is the magnitude of the electric flux of a constant electric field of $4\,{\rm N/C}$ in the $z$-direction through a rectangle with a surface area of $4\,{\rm m^2}$ in the $xy$-plane?
Solution: To calculate the electric flux, we need the magnitude of the electric field, the area of the surface, and the angle between $\vec{E}$ and the normal vector to the surface. Here, $\vec{E}=4\,\hat{k}\,{\rm N/C}$ and area $A=4\,{\rm m^2}$ are given explicitly, but the angle isn't.
When a flat surface spans the $xy$-plane, the vector perpendicular to it points in either the positive or negative $z$-direction. In this case, we were told that the electric field points in the positive $z$-direction, but the direction of the normal vector hasn't been specified.
In this case, to find the electric flux, we choose one of the above directions, say up. Thus, the angle between $\vec{E}$ and $\hat{n}$ is $\theta=0$. The flux is then calculated as follows: \begin{align*} \Phi_e&=EA\,\cos \theta\\&=4\times 4\times \underbrace{\cos 0^\circ}_{1}\\&=\boxed{16\quad {\rm N \cdot m^2/C}}\end{align*} This means the electric field is $16\,\rm N \cdot m^2/C$.
Problem (6): At the center of a sphere of radius $0.5\,\rm m$ a point charge of $2\,\rm \mu C$ is placed. What electric flux is passing through the sphere?
Solution: Electric flux is defined as the product of $E_{\bot}$ and the area surface $A$ \[\Phi_E=E_{\bot}A\] where $E_{\bot}$ is the component of $\vec{E}$ perpendicular to the surface.
In this problem, we first calculate the magnitude of the electric field created by the point charge at the location of the given surface with radius $r=0.5\,\rm m$: \begin{align*} E&=k\frac{q}{r^2} \\\\ &=(8.99\times 10^9) \frac{2\times 10^{-6}}{(0.5)^2}\\\\ &=71920\,\rm N/C \end{align*} These field lines point radially outward and are everywhere perpendicular to the sphere's surface. It's important to note that the magnitude of the electric field obtained is the same throughout the surface of the sphere.
Substituting the numerical values into the electric flux formula, we get: \begin{align*} \Phi_E &=EA=E(4\pi r^2) \\ &=(71920) \times 4\pi (0.5)^2 \\ &=\boxed{2.26\times 10^5 \quad\rm N\cdot m^2/C} \end{align*} where $A=4\pi r^2$ is the area surface of the sphere of radius $r$. Consequently, roughly $226000$ field lines are penetrating the surface of this sphere.
we can see this question from the perspective of Gauss's law problem. Gauss's law and the electric field are closely related. According to this law, we have: \[\text{flux}=EA\cos\theta=\frac{Q_{inside}}{\epsilon_0}\] where $Q_{inside}$ is the net charge inside a closed surface and $\epsilon_0=8.85\times 10^{-12}\,\rm C^2/N\cdot m^2$.
In this case, substituting the numerical values into the above formula, we get: \begin{align*} \text{flux}&=\frac{Q_{inside}}{\epsilon_0} \\\\ &=\frac{2\times 10^{-6}}{8.85\times 10^{-12}} \\\\ &=226000\quad \rm N\cdot m^2/C \end{align*} It's worth noting that Gauss's law is applicable when we want to calculate the flux through a closed surface.
Problem (7): A $2\,{\rm cm} \times 2\,{\rm cm}$ square lies in the $xy$-plane. Find the electric flux through the square for each of the following electric field vectors.
(a) $\vec{E}=(50\,\hat{i}+20\,\hat{j})\,{\rm N/C}$
(b) $\vec{E}=(50\,\hat{k}+20\,\hat{j})\,{\rm N/C}$
Solution: In this electric flux problem, we want to use the concept of the scalar product to find the magnitude of the flux. According to this concept, the electric flux of a uniform electric field through a flat surface is defined as the scalar product of electric field $\vec{E}$ and the area vector $\vec{A}=A\,\hat{n}$, where $\hat{n}$ is a vector perpendicular to the surface (the normal vector) and points outward.
Here, the surface through which we want to find the flux lies in the $xy$-plane. The normal vector to a surface on the $xy$-plane is parallel to $z$-axis which is shown as $\hat{n}=(x=0,y=0,z=1\,\hat{k})$.
Recall that the scalar product of two vectors $\vec{A}=A_x \hat{i}+A_y \hat{j}$ and $\vec{B}=B_x \hat{i}+B_y \hat{j}$ is given as \[\vec{A}\cdot \vec{B}=A_x B_x+A_y B_y\]
(a) Therefore, the electric flux through a flat surface on the $xy$-plane is \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=\vec{E}\cdot \vec{A} \\&=(50\,\hat{i}+20\,\hat{j})\cdot (+\hat{k})\\&=50\,\underbrace{\hat{i}\cdot\hat{k}}_{0}+20\,\underbrace{\hat{j}\cdot\hat{k}}_{0}\\&=0 \end{align*}
(b) Again, we have \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=\vec{E}\cdot \vec{A} \\&=(50\,\hat{k}+20\,\hat{j})\cdot (+\hat{k})\\&=50\,\underbrace{\hat{k}\cdot\hat{k}}_{1}+20\,\underbrace{\hat{j}\cdot\hat{k}}_{0}\\&=50\quad {\rm N.m^2/C} \end{align*}
To find out how to compute $\hat{i}\cdot \hat{j}=0$ or $\hat{i}\cdot\hat{i}=1$ and so on, refer to the page of unit vector problems.
Problem (8): A circle of radius $3\,{\rm m}$ lies in the $yz$-plane in the presence of a uniform electric field of $\vec{E}=(100\hat{i}+200\hat{j}-50\hat{k})\,{\rm N/C}$. Find the electric flux through this circle.
Solution: In the context of a circle lying in the $yz$-plane, any vector perpendicular to the circle's surface and pointing either outwards or inwards will be parallel to the $x$-axis.
Consequently, the normal vector to this surface can be expressed as either $+\hat{i}$ or $-\hat{i}$.
It's important to note that both directions yield the same magnitude for the electric flux calculation. Choosing $\hat{n}=\hat{i}$, the area vector can be written as $\vec{A}=A\,\hat{n}$ where $A=\pi r^2$ is the area of the circle.
Note: the normal vector on an open surface can point in either direction. In this case, we must choose one of them.
By definition of electric flux as the dot product of $\vec{E}$ and the area vector $\vec{A}$, we will have \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=\vec{E}\cdot \vec{A} \\&=(100\,\hat{i}+200\,\hat{j}-50\,\hat{k})\cdot (A\,\hat{i})\\&=100\,A\,(\underbrace{\hat{i}\cdot\hat{i}}_{1})+200\,A\,(\underbrace{\hat{j}\cdot\hat{i}}_{0})-50\,A\,(\underbrace{\hat{k} \cdot \hat{i}}_{0})\\ & =100\,A\\&=100\,\pi\,(3)^2\\&=\boxed{2827.5\quad {\rm N\cdot m^2/C}} \end{align*} In above the area of the circle is found as $A=\pi r^2=\pi\times 3^2$.
Problem (9): A flat surface with an area of 20 squared meters lies in the $xz$-plane where a uniform electric field of $\vec{E}=5\hat{i}+4\hat{j}+5\hat{k}$ exists. Find the electric flux through this surface.
Solution: Again the surface through which the flux is calculated lies in the $xz$-plane. A unit vector perpendicular (normal vector) to the $xz$-plane is parallel to the $y$-axis, so we can choose, say the positive $y$-direction, $\hat{n}=(0,1,0)$. The definition of electric flux says that the scalar product of electric field $\vec{E}$ and the area vector $\vec{A}=A\hat{n}$ gives the number of electric field lines passing through a surface, therefore we have \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=\vec{E}\cdot \vec{A}\\&=(5\,\hat{i}+4\,\hat{j}+5\hat{k})\cdot (A\,\hat{j})\\&=4A\\&=4(20)=80\quad {\rm N.m^2/C} \end{align*}
Problem (10): The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by $\vec{E}=\sqrt{3}\hat{i}-\hat{j}\quad \Big({\rm \frac Vm}\Big)$. A square frame of side 1 meter is shown in the figure. Point N lies in the $x-y$-plane. The initial angle between line ON and the x-axis is $60^\circ$. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through the area enclosed in the square frame LMNO.
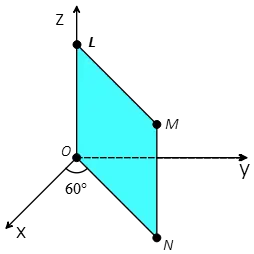
Solution: This electric flux question is a little more difficult and is designed for the AP Physics C exam. First, determine the normal vector to the given surface LMNO as shown in the top view of the figure below. As you can see, the perpendicular vector is $\hat{n}=\sin \theta (-\hat{i})+\cos \theta (+\hat{j})$ where $\theta$ is shown in the figure.
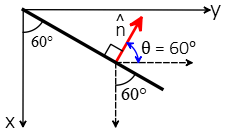
Now using the definition of electric flux, $\Phi_e=\vec{E}\cdot\vec{A}$ where $\vec{A}=A\,\hat{n}$ is the area vector, we will have \begin{align*} \Phi_e &=\vec{E}\cdot\vec{A}\\&=(\sqrt{3}\hat{i}-\hat{j})\cdot \Big(A\,\sin \theta (-\hat{i})+A\,\cos \theta (+\hat{j})\Big)\\&=-A\sqrt{3}\sin 60^\circ (\underbrace{\hat{i}\cdot \hat{i}}_{1})-A\cos 60^\circ\,(\underbrace{\hat{j}\cdot\hat{j}}_{1})\\&=-A\sqrt{3}\,\frac{\sqrt{3}}2 - A\,\frac 12\\&=-2A\\&=-2(1 \times 1)\\&=-2 \quad {\rm N\cdot m^2/C}\end{align*} where $A$ is the area of a square of edge $1$ meter. The negative value of electric flux indicates that the electric field and the normal vector are in the opposite direction or the field lines are going into the given surface.
The electric flux of non-uniform electric fields:
Problem (11): A non-uniform electric field is given by the expression \[\vec{E}=ay\hat{i}+bz\hat{j}+cx\hat{k}\] Where $a,b,c$ are constants, $\hat{i},\hat{j},\hat{k}$ are unit vectors in the $x,y,z$ directions, respectively. Determine the electric flux through a rectangular surface in the xy-plane, extending from $x=0$ to $x=w$ and from $y=0$ to $y=h$.
Solution: The electric flux of a non-uniform electric field through any surface is defined to be in integral form as \[{\Phi }_e=\oint_S{\vec{E}\cdot\hat{n}dA}\] Where $S$ stands for the surface we are integrating over, $\hat{n}$ is the unit vector normal to the surface and $\vec{E}$ is the electric field over the surface.
In this case, since the surface lies in the xy-plane, so unit vector normal to it is $\hat{n}=\hat{k}$ \begin{align*} {\Phi }_e&=\oint_S{\vec{E}\cdot \hat{n}\,dA}\\ &=\int{\Big(ay\hat{i}+bz\hat{j}+cx\hat{k}\Big) \cdot (dx\,dy \hat{k})} \\ &=c\,h\,{\Big(\frac{1}{2}x^2\Big)}^w_0\\ &=\frac{1}{2}chw^{2} \end{align*}
Problem (12): The cubical surface of side length $L=12\ {\rm cm}$ is positioned into an electric field of $\vec{E}=\left(950\,y\,\hat{i}+650\,z\,\hat{k}\right)\ {\rm V/m}$. Find the electric flux through the top face of the cube.
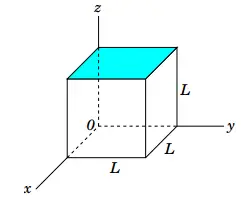
Solution: By definition, the electric flux passing through any surface $A$ is the number of field lines penetrating it. In the mathematical form \[\Phi_e=\int_S{\vec{E}\cdot \hat{n}dA}\] Where $\hat{n}$ is the unit vector normal to the surface $A$.
In this problem, the normal vector is parallel to the z-axis that is $\hat{n}=\hat{k}$. So
\begin{align*} \Phi_e&=\int{\left(950\,y\, \hat{i}+650\, z\,\hat{k}\right)\cdot\hat{k}\ dA}\\ &=\int{\Big(950\, y\,(\underbrace{\hat{i}\cdot \hat{k}}_{0})+650\, z\, \underbrace{\hat{k}\cdot \hat{k}}_{1})\Big)\,(\underbrace{dx\,dy}_{dA})}\\ &=650\,(0.12)\int{dxdy} \end{align*} Where the last integral is the area of the surface which is integrated over. Thus the total flux through the given surface is
\begin{align*} \Phi_e &=650(0.12)L^2\\&=650\times (0.12)^3\\&=1.1232\quad {\rm N.m^2/C}\end{align*}
Problem (13): A hemispherical shell of radius R is placed in an electric field E which is parallel to its axis. What is the flux $\Phi_E$ of the electric field through the shell?
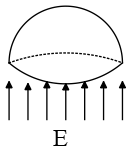
Solution: By definition, the electric flux passing through any surface with area element $dA$ is the integral of the scalar product of the normal component of the electric field and area of the given surface that is \[{\Phi}_e=\int_S{\vec{E}\cdot \hat{n}\, dA}\] Where $\hat{n}$ is the unit vector normal to the surface and $S$ is the surface over which the integral is evaluated.
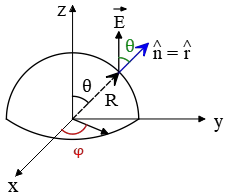
In the case of hemisphere or sphere, the unit vector is along the radius i.e. $\hat{n}=\hat{r}$. Since $\vec{E}$ is perpendicular to the plane of the great circle of the hemisphere so the scalar product of $E$ and $\hat{r}$ is $E{\cos \theta\ }$. The range of polar angle is from $\theta=0$ to $\theta=\pi/2\ $. Therefore,
\begin{align*} {\Phi }_e&=\int^{\frac{\pi}{2}}_0{\vec{E}\cdot \hat{r}dA} \\&= \int^{2\pi}_0{d\phi}\int^{\frac{\pi}{2}}_0{E\,{\cos \theta\ }\ R^2\,{\sin \theta\ }d\theta}\\ &= 2\pi ER^2\int^{\frac{\pi}{2}}_0{\underbrace{{\sin \theta\ }{\cos \theta\ }}_{\frac{1}{2}{\sin 2\theta\ }}d\theta}\\ &=2\pi ER^2\left(\frac{1}{2}\right){\left(-\frac{1}{2}{\cos 2\theta\ }\right)}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}_0\\ &=-\frac{1}{2}\pi ER^2\left({\cos 2\frac{\pi}{2}\ }-{\cos 0\ }\right)\\&=\pi ER^2 \end{align*} In above, $dA=R^2\,{\sin \theta\ }d\theta d\phi $ is the area element of the sphere.
Alternate Solution: All of the electric field lines through the circle at the bottom of the hemisphere pass through the area of the hemisphere as well. So by calculating the flux through the circle, one can find the flux through the hemisphere but the important thing to remember is that, by convention, the flux through the circle is incoming and negative of the outgoing flux through the hemisphere that is ${\Phi }_e\left(circle\right)=-{\Phi}_e(hemisphere)$.
Therefore, by definition of the electric flux through a surface, we get \begin{align*} {\Phi }_e \left(circle\right)&=\vec{E}\cdot \hat{n}\,A\\&=E\,(+\hat{k})\cdot (-\hat{k})\,(\pi R^2)\\&=-\pi ER^2\end{align*} Note: the normal vector $\hat{n}$ is defined always in the outward direction of the surface.
Problem (14): A rectangular flat surface is placed on the $xy$-plane. In this region of space, there is a non-uniform electric field of $\vec{E}=E_0 x^2 \hat{k}$, where $E_0$ is a constant. What is the electric flux through the rectangular surface?
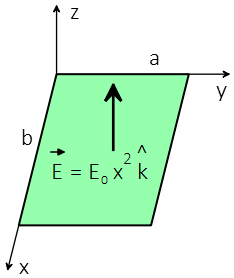
Solution: Since the electric field is not constant over the surface so the integral definition of electric flux must be used. To use this method, we must first construct an area element such that the electric field is constant across it. In this problem, along the y-direction, $\vec{E}$ is constant so we choose a strip with an area of $dA=a\,dx$.
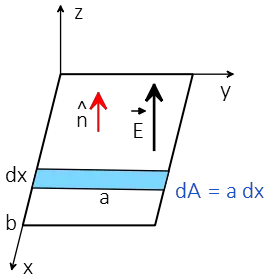
Thus we get the net electric flux through this open surface as below \begin{align*} \Phi_e&=\int_S{\vec{E}\cdot \hat{n}\,dA}\\&=\int_0^b{\Big(E_0\,x^2\hat{k}\Big)\cdot \hat{k}(a\,dx)}\\&=E_0\,a\int_0^b{x^2 dx}\\&=aE_0 \Big(\frac 13 x^3\Big)_0^b\\&=\frac 13 aE_0\,b^3 \end{align*}
Problem (15): An square of side $L$ lies in the $xy$-plane. The electric field crosses the square in the $z$-direction as $\vec{E}=\frac {E_0}{a}\,y\,\hat{k}$. What is the electric flux through the surface as shown in the figure?
Solution: remember that the electric flux is a surface integral. Take an infinitesimal strip of width $dy$ and length $L$ so that the electric field over it is constant. Consequently, the area vector becomes $d\vec{A}=a\,dy\,\hat{k}$. Therefore, the integral form of definition of electric flux gets \begin{align*} \Phi_e&=\int_S{\vec{E}\cdot\hat{n}\,dA}\\&=\int{(\frac {E_0}{a}\,y\,\hat{k})\cdot (a\,dy\,\hat{k})}\\&=\frac {E_0}{a}\,a\int_{0}^{a}{y\,dy}\\&=\frac {E_0}{a}\,a\,\Big(\frac 12 y^{2}\Big)_0^{a}\\&=\frac 12 E_0 a^2 \end{align*}
Note: for a non-uniform electric field, the integral definition of electric flux must be used.
All of the above electric flux problems are suitable for high schools and colleges. In all these problems, we used the direct definition of flux to compute it.
Author: Dr. Ali Nemati
Date Created: 10/24/2020
Last Update: 2/10/2022
© 2015 All rights reserved. by Physexams.com
AP® is a trademark registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse, this website.
